Lesson 8: DeFi Lending and Borrowing
Lesson 8: DeFi Lending and Borrowing
🎯 Core Concept: Over-Collateralized Lending
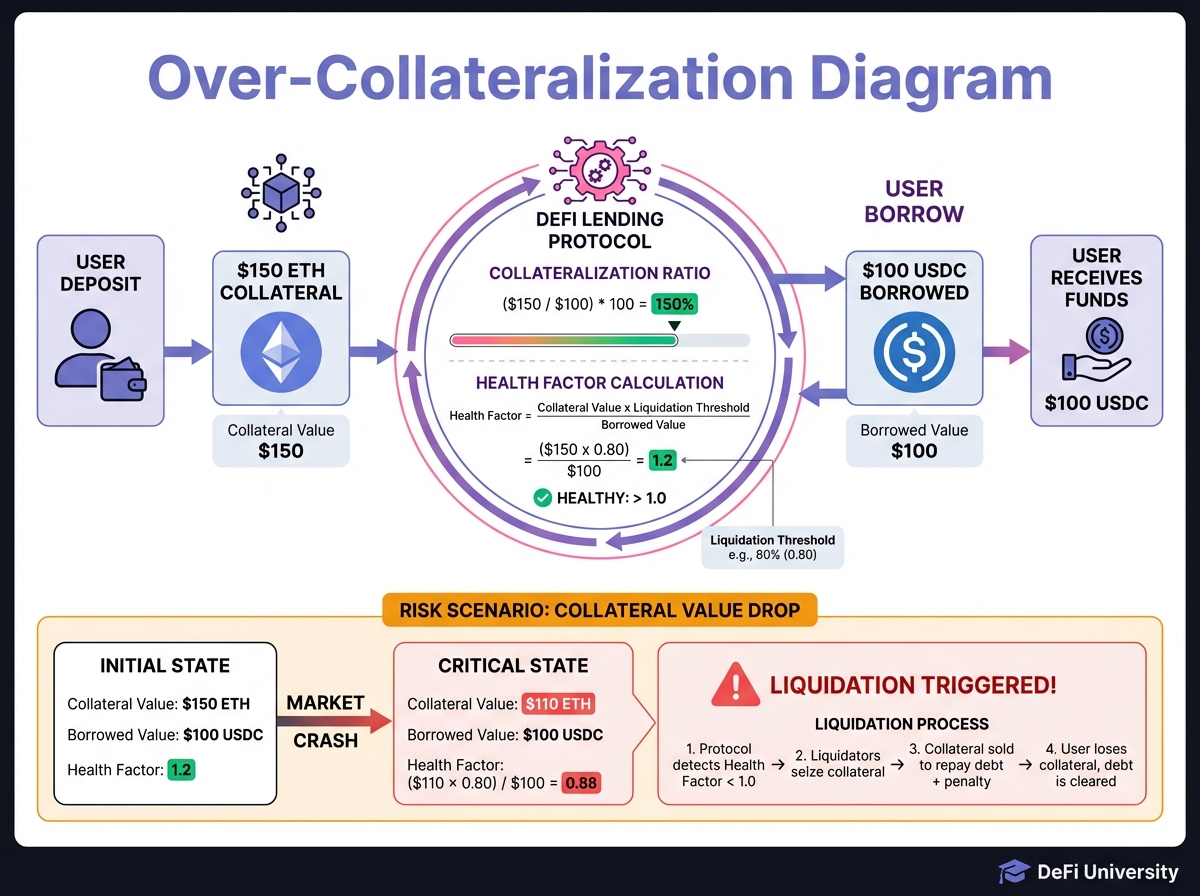
📚 How It Works
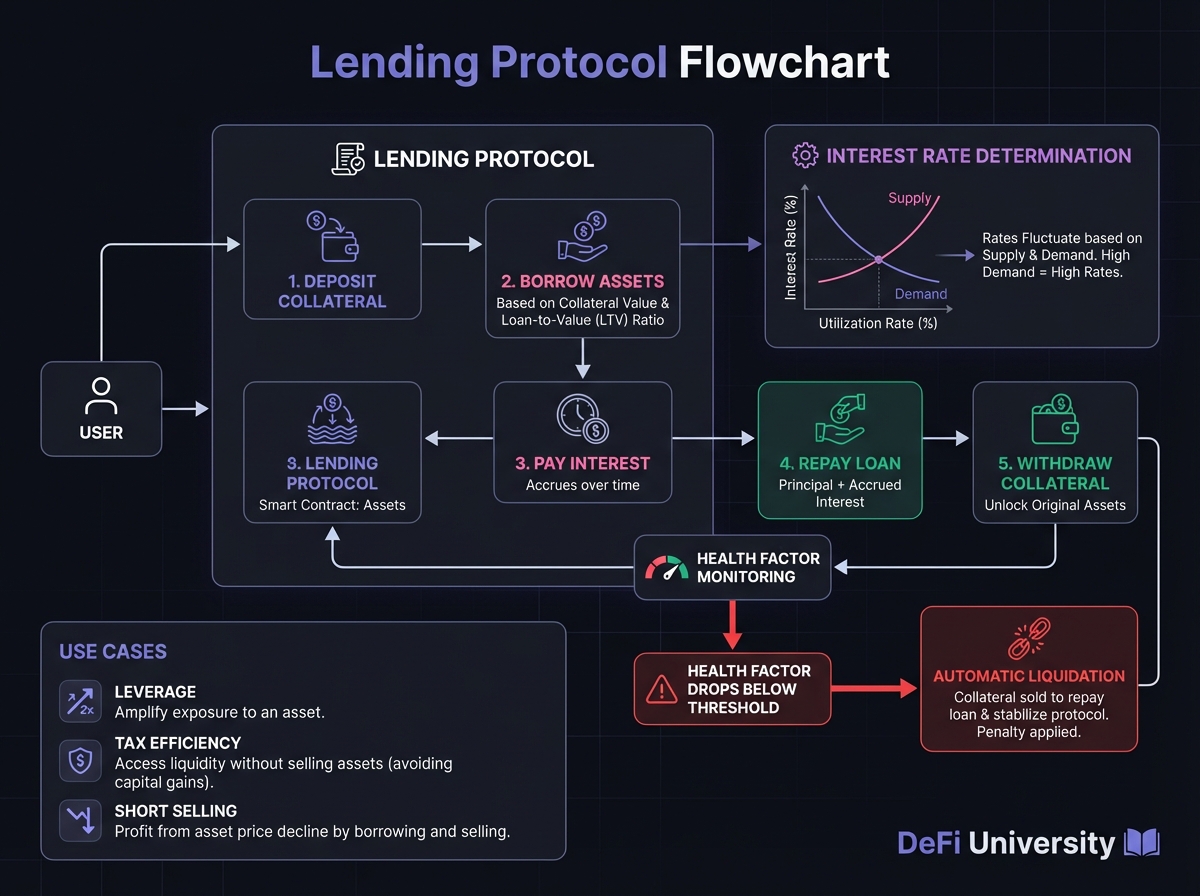
📚 Health Factors
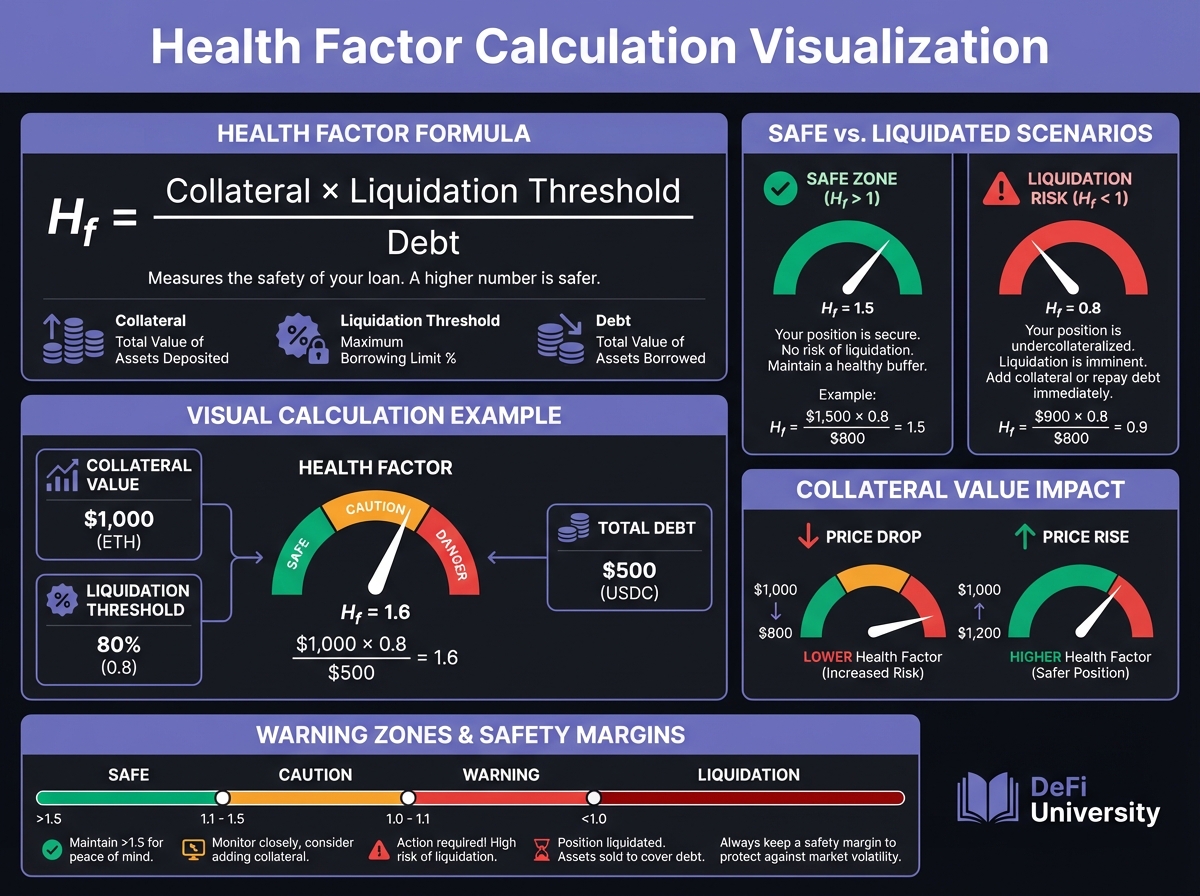
🎮 Interactive: Lending Calculator
Interactive DeFi Protocol Explorer
🔑 Key Takeaways
Last updated