Lesson 10: MEV, JIT Liquidity, and Advanced Tactics
🎧 Lesson Podcast
🎬 Video Overview
Lesson 10: MEV, JIT Liquidity, and Advanced Tactics
🎯 Core Concept: The Dark Forest of DeFi
🔍 Understanding MEV
What is MEV?
How MEV Affects LPs
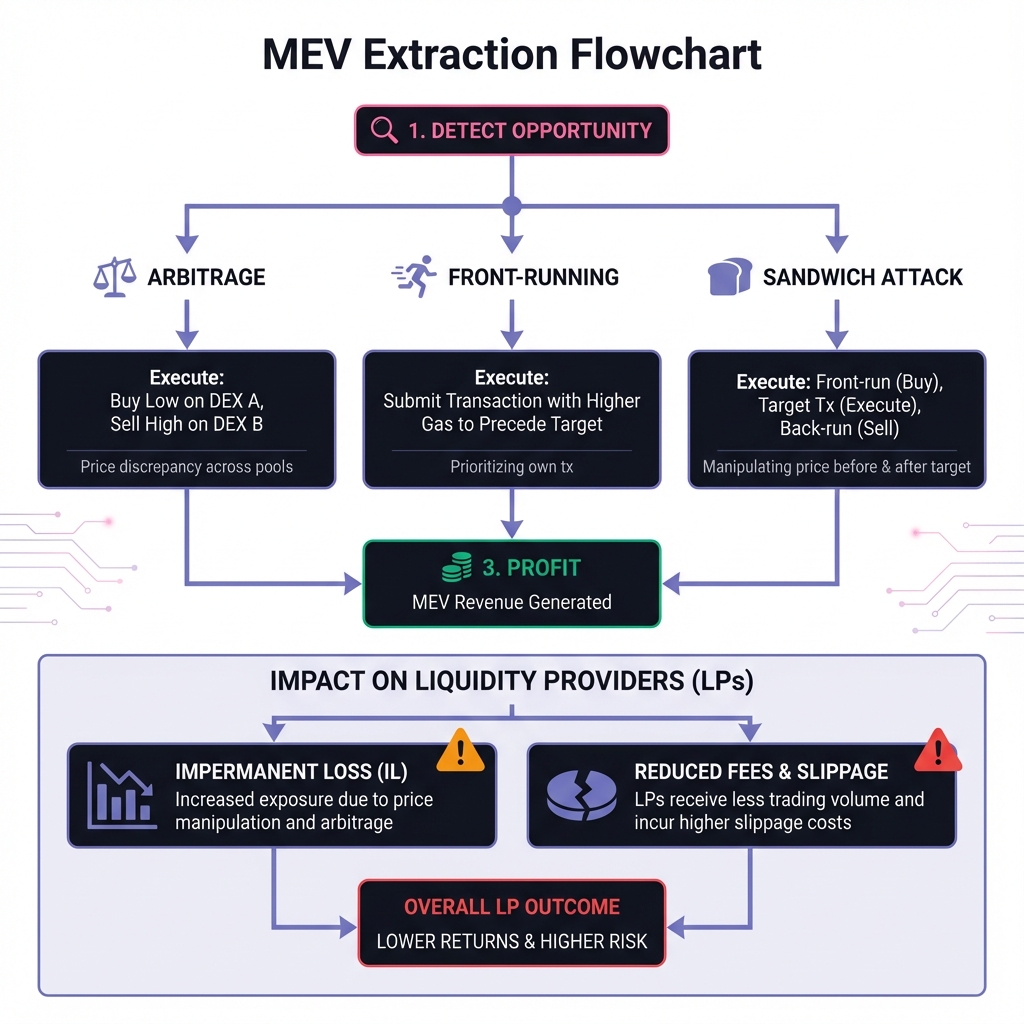
⚡ Just-In-Time (JIT) Liquidity
The JIT Attack
JIT Example
JIT Frequency
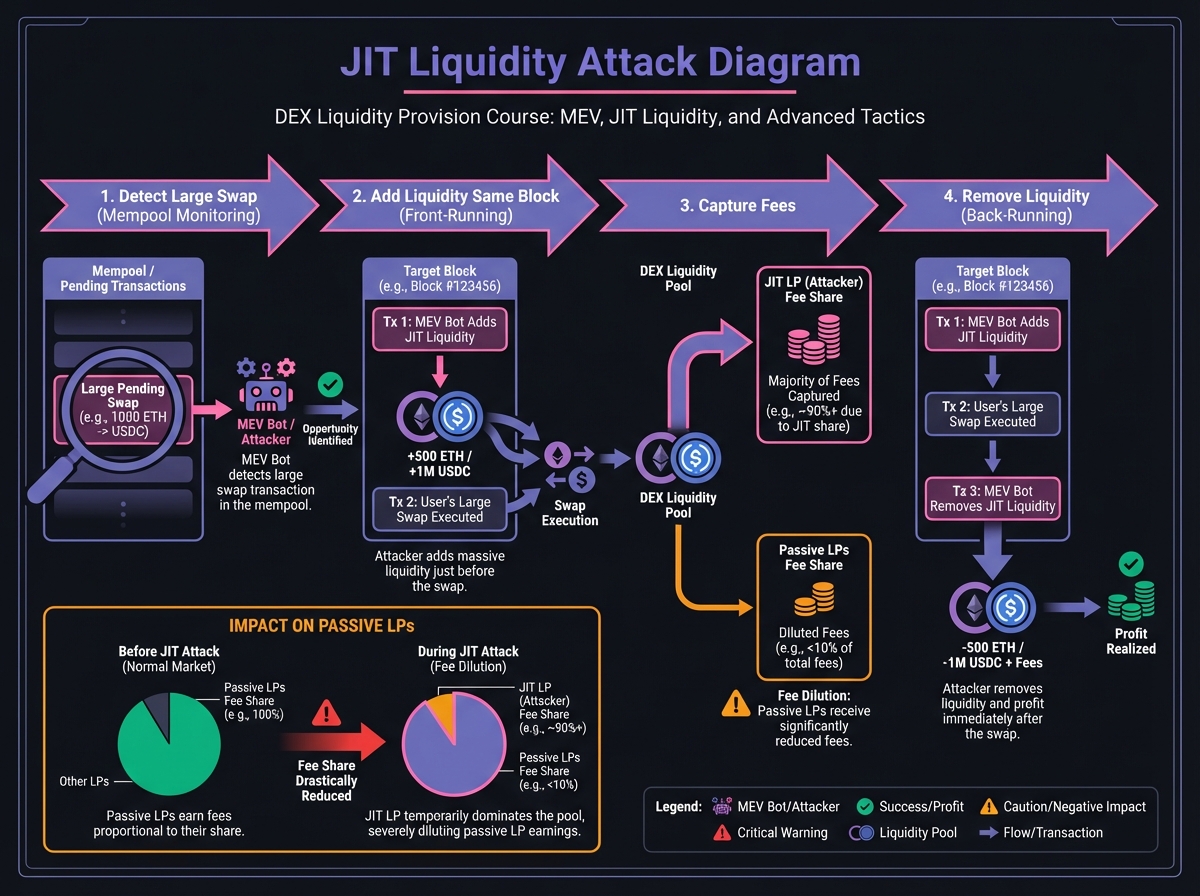
🛡️ Protecting Against MEV/JIT
Strategy 1: Use Private Pools
Strategy 2: Use DEX Aggregators
Strategy 3: Wider Ranges (V3)
Strategy 4: Use L2s or Alternative Chains
🔬 Advanced Deep-Dive: Participating in MEV
Can LPs Participate in MEV?
MEV Bot Requirements
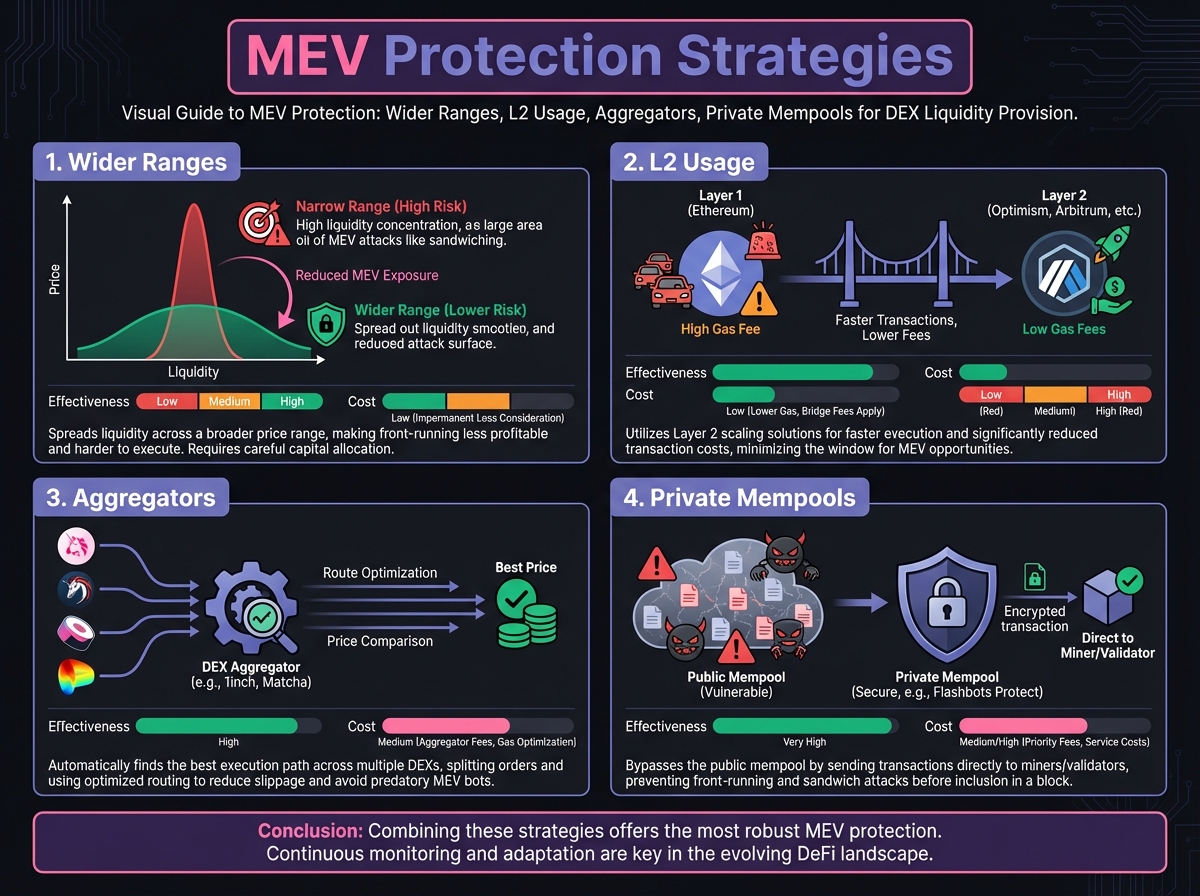
📊 MEV Impact Analysis
Measuring MEV Impact
Typical Impact
🎓 Beginner's Corner: MEV Basics
🔑 Key Takeaways
🚀 Next Steps
PreviousExercise 9: V4 Hooks and ALM IntegrationNextExercise 10: MEV Analysis and Protection Strategies
Last updated