Lesson 7: Drift Protocol - Solana's Hybrid Architecture
🎧 Lesson Podcast
🎬 Video Overview
Lesson 7: Drift Protocol - Solana's Hybrid Architecture
🎯 Core Concept: The Liquidity Trifecta
Why Drift Matters
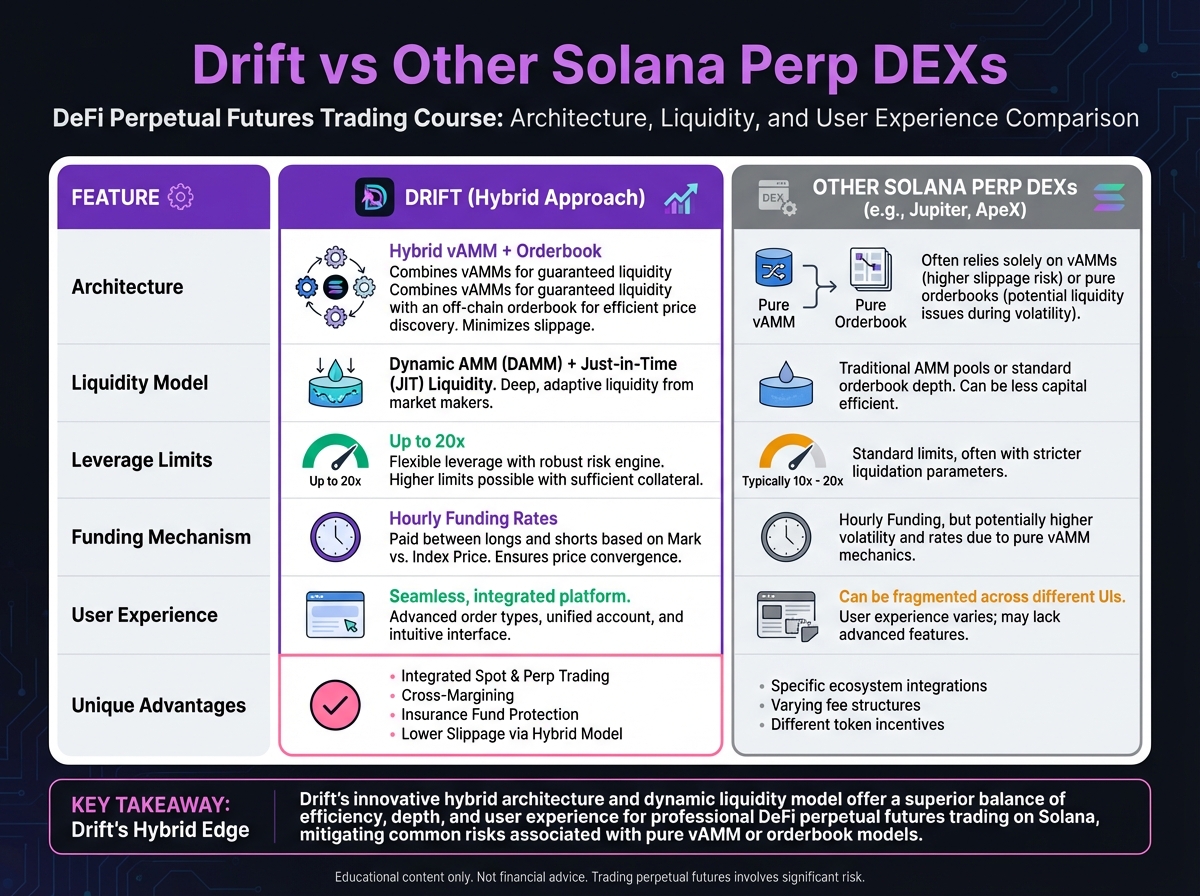
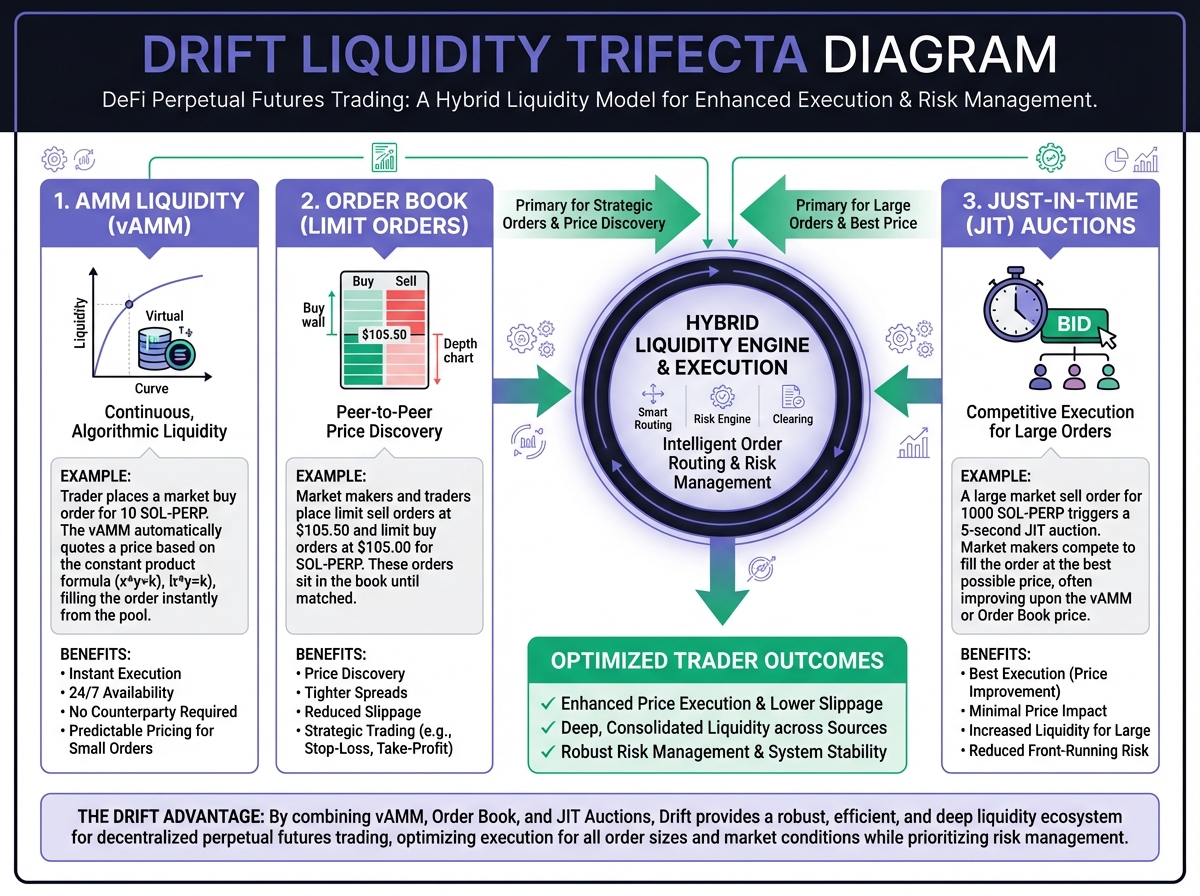
🏗️ The Liquidity Trifecta Architecture
Layer 1: Just-In-Time (JIT) Auction
Layer 2: Decentralized Limit Orderbook (DLOB)
Layer 3: Dynamic AMM (DAMM)
🔄 Trade Execution Lifecycle
The Waterfall Process
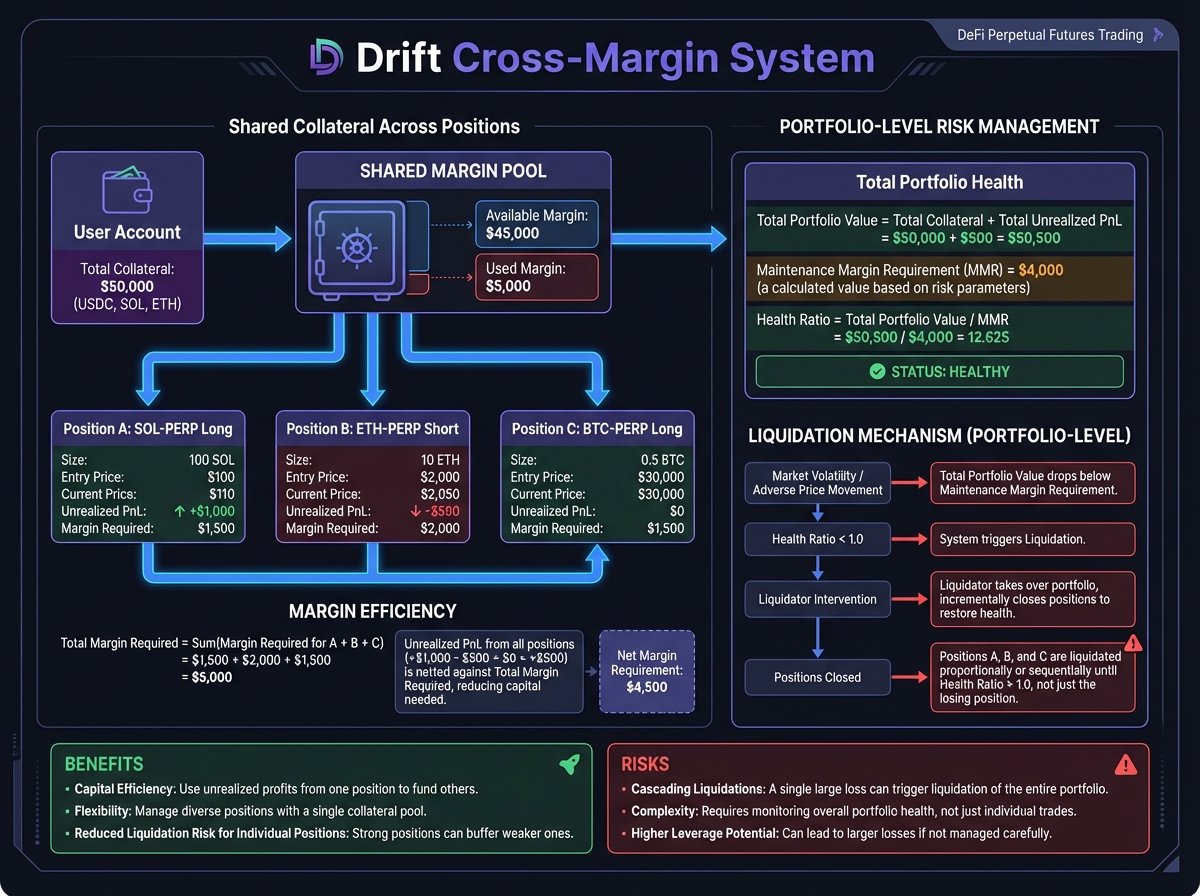
💰 Cross-Margin System
Unified Margin Across Products
Asset Weightings
Asset Type
Example
Initial Weight
Maintenance Weight
Cross-Margin Benefits
🎓 Beginner's Corner: Using Drift
Getting Started
Opening a Position
🔬 Advanced Deep-Dive: JIT Auction Mechanics
The Dutch Auction Formula
MEV Internalization
⚠️ Risks and Considerations
Solana-Specific Risks
Cross-Margin Risks
Keeper Network Risk
📊 Real-World Example: Trading on Drift
⚖️ Compare Protocols
🔑 Key Takeaways
🚀 Next Steps
PreviousExercise 6: GMX V2 Market Analysis and SelectionNextExercise 7: Drift Market Creation and Strategy Analysis
Last updated