Exercise 1: AMM Fundamentals Assessment
🔍 Phase 1: Knowledge Check (10 minutes)
Understanding Check
📊 Phase 2: Calculation Practice (15 minutes)
Swap Calculation Exercise
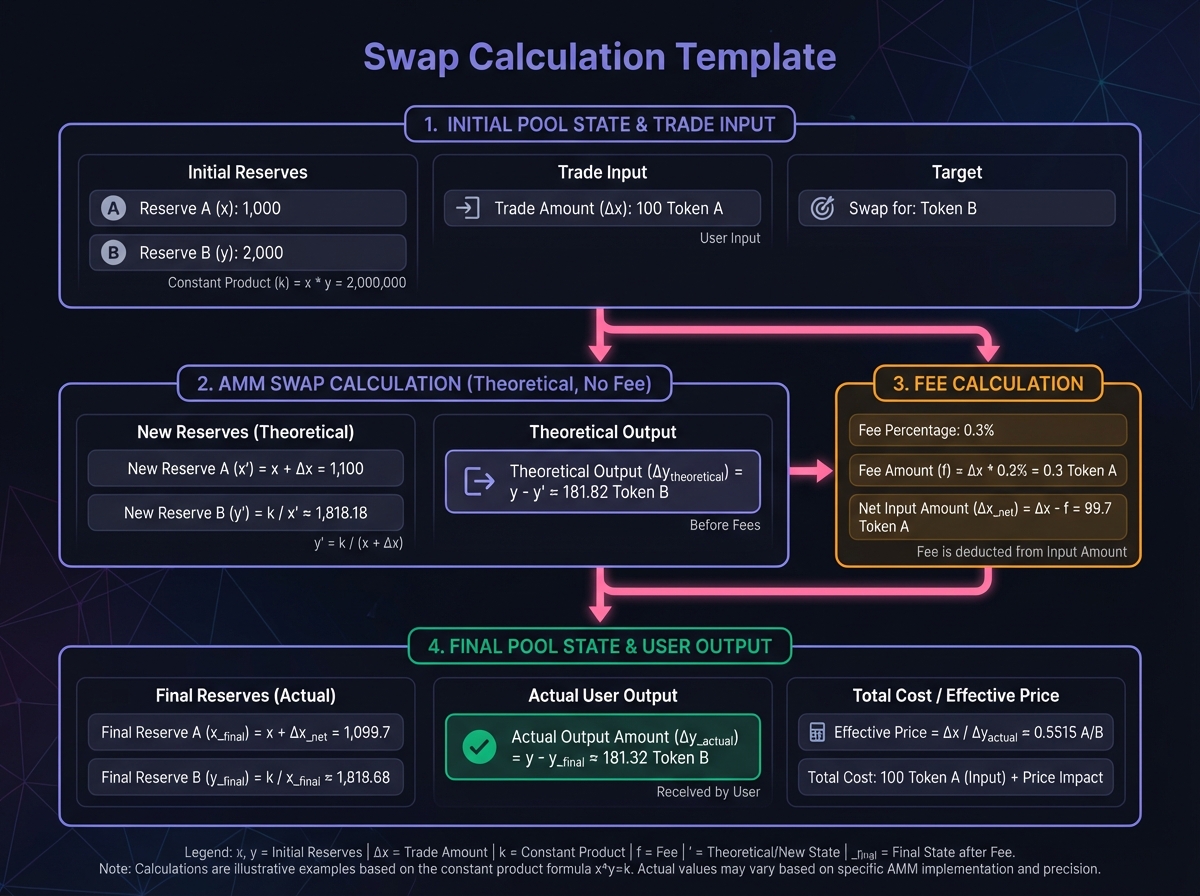
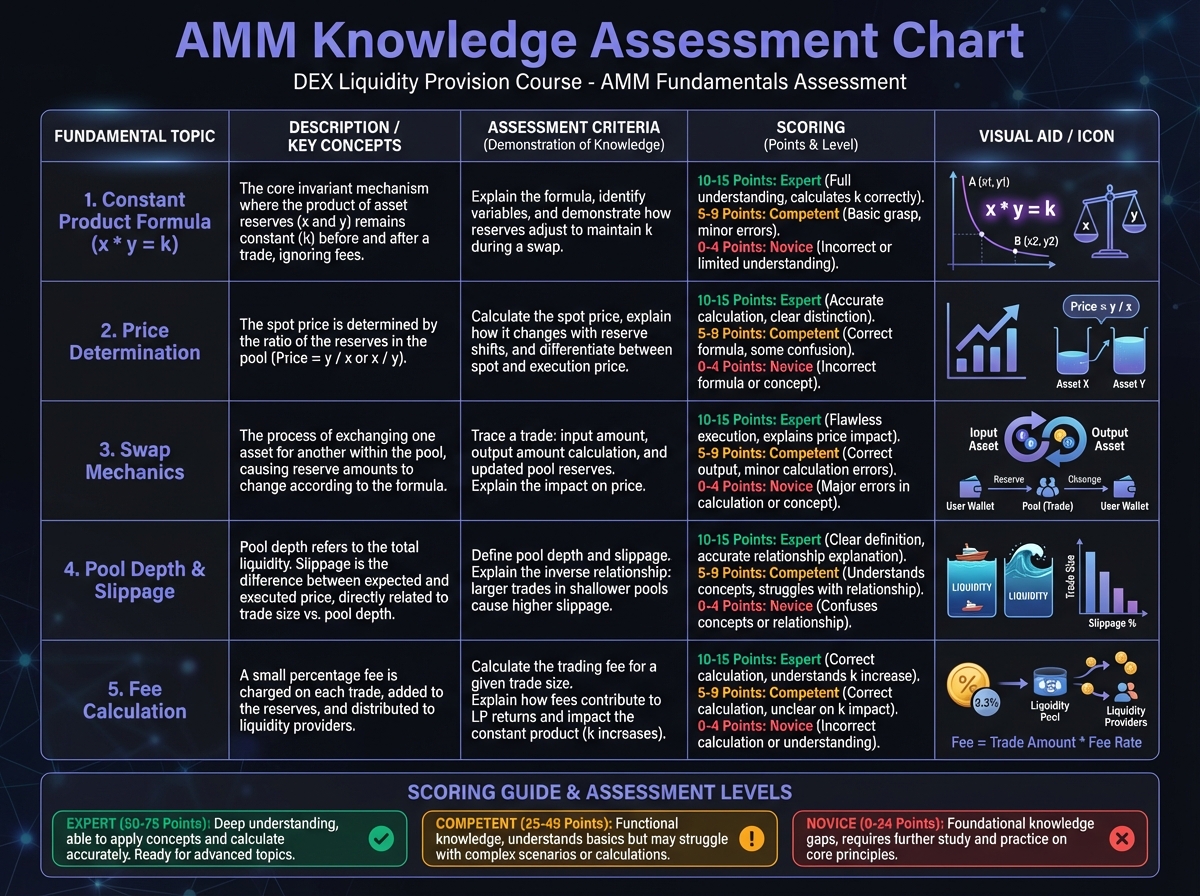
Pool Depth Exercise
💡 Phase 3: Real-World Application (10 minutes)
Pool Selection Exercise
🎯 Phase 4: Self-Assessment (10 minutes)
Knowledge Score
Gap Identification
📚 Next Steps
PreviousLesson 1: Understanding AMM FundamentalsNextLesson 2: The Mathematics of Liquidity Provision
Last updated