Lesson 10: Risk Management and Hedging
🎧 Lesson Podcast
🎬 Video Overview
Lesson 10: Risk Management and Hedging
🎯 Core Concept: Professional Risk Management
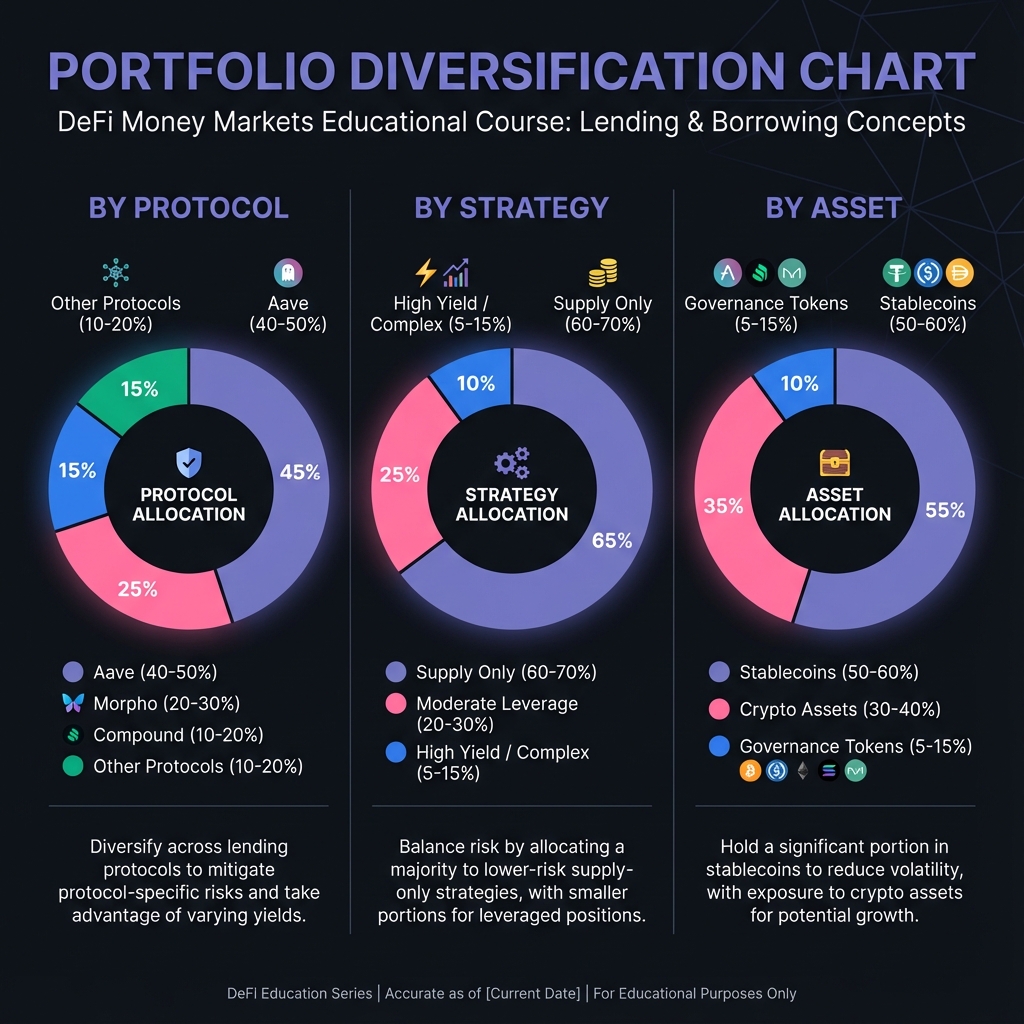
📊 Portfolio Diversification
Multi-Protocol Strategy
Correlation Analysis
🛡️ Liquidation Protection Strategies
Health Factor Monitoring Systems
Dynamic Collateral Management
Automated Protection Mechanisms
🔄 Hedging Strategies
Understanding Hedging
Common Hedging Techniques
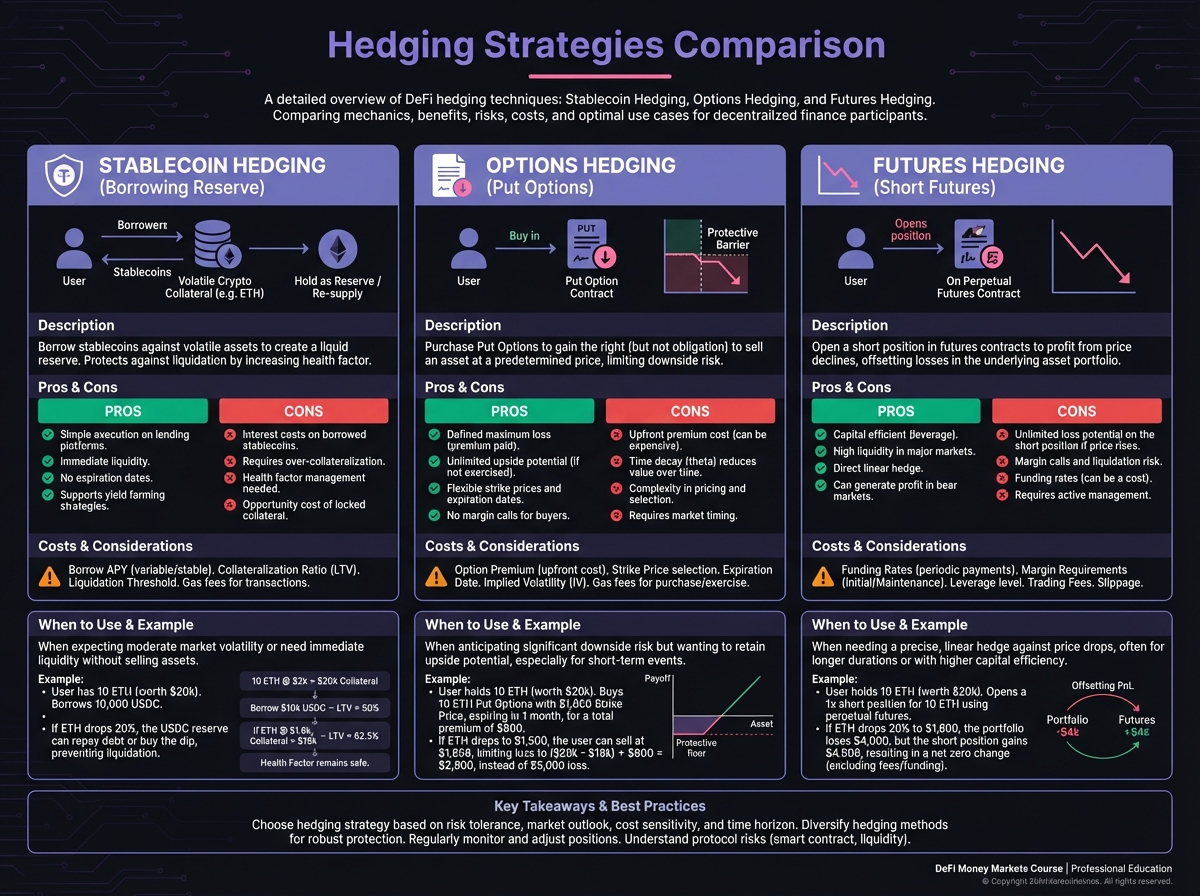
Partial Hedging
🏗️ Risk Management Framework
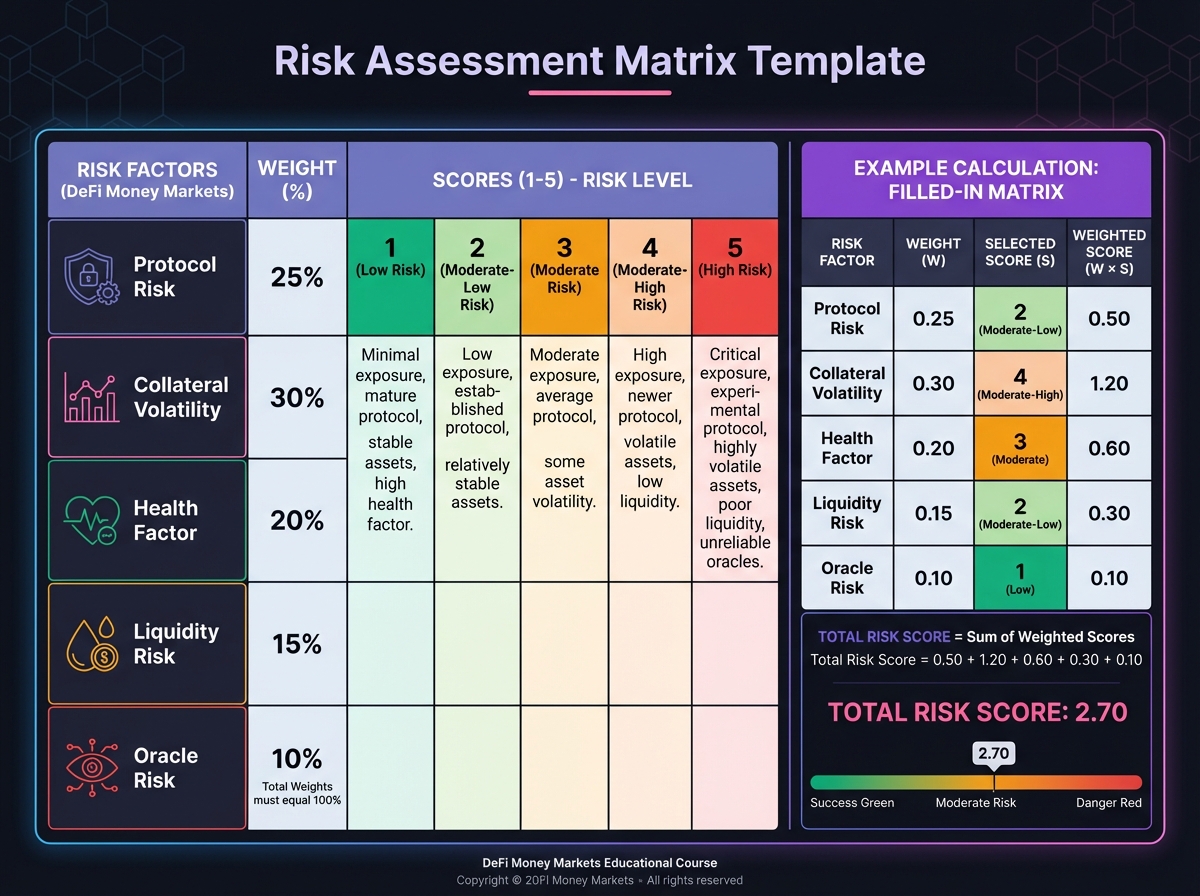
Risk Assessment Matrix
Factor
Score (1-5)
Weight
Weighted Score
Position Sizing Framework
Stress Testing
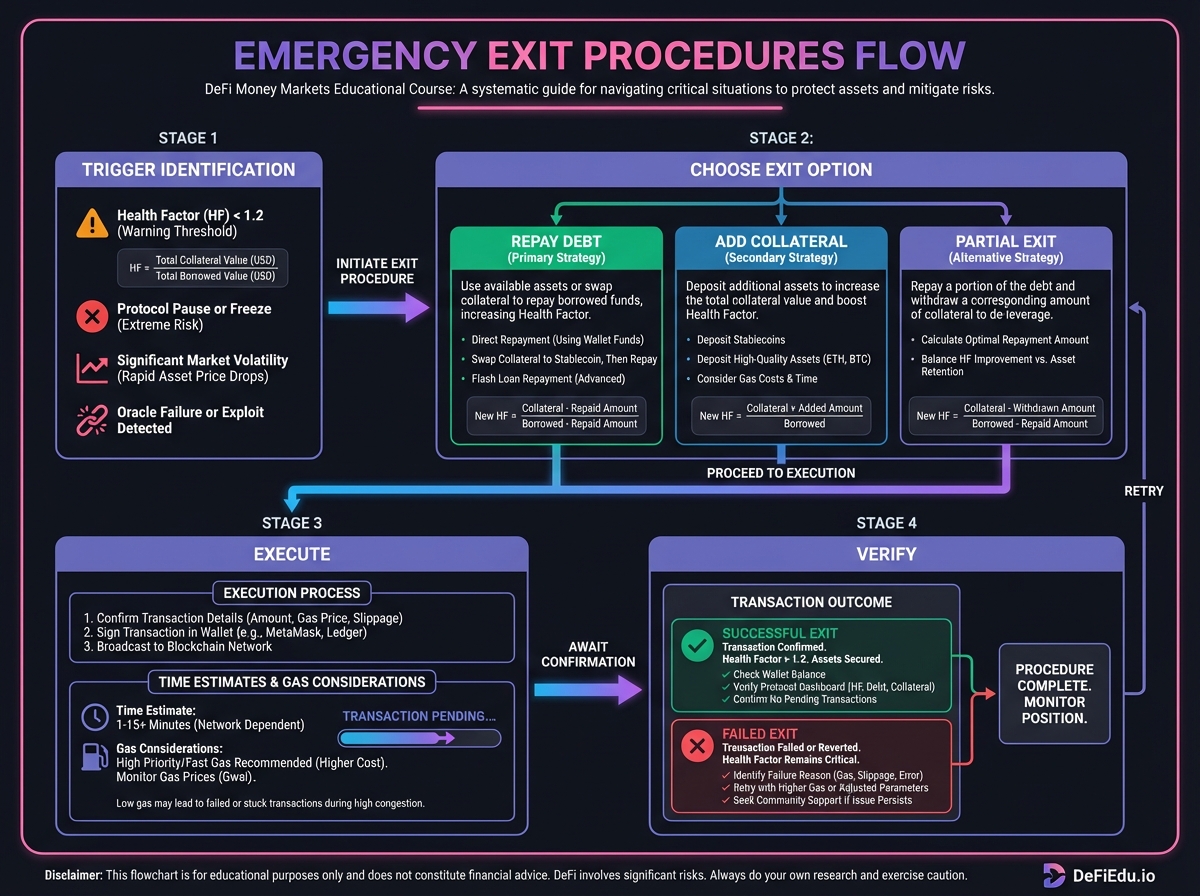
🚨 Emergency Exit Procedures
When to Exit
Exit Execution
Exit Timing
📈 Risk-Adjusted Returns
Sharpe Ratio (Simplified)
Sortino Ratio
🎯 Risk Management Best Practices
Daily Practices
Weekly Practices
Monthly Practices
🎓 Beginner's Corner
🔬 Advanced Deep-Dive: Correlation Hedging
Portfolio Correlation Matrix
📊 Real-World Example: Risk Management
Interactive Risk Assessment Checklist
🔑 Key Takeaways
🚀 Next Steps
Last updated